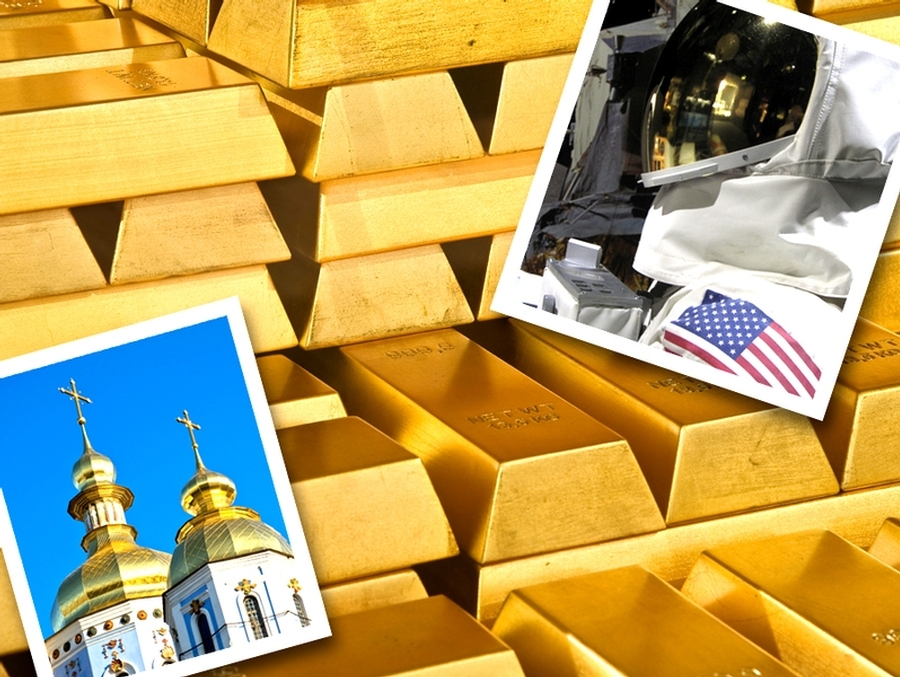
Gold’s qualities make it one of the most coveted metals in the world. Not only can it be beautifully shaped and sculpted, the yellow metal conducts electricity and does not tarnish. These qualities make it the metal of choice for a wide variety of industries. Let’s take a look at some industrial, medical and technological uses of gold, some of which are truly amazing.
 Gold has been used in dentistry for nearly 3,000 years. The first book published on dentistry, entitled Artzney Buchlein, appeared in 1530. The book suggests dentists fill cavities and rotten teeth with gold leaf.
Gold has been used in dentistry for nearly 3,000 years. The first book published on dentistry, entitled Artzney Buchlein, appeared in 1530. The book suggests dentists fill cavities and rotten teeth with gold leaf.
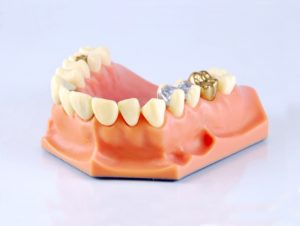 Thousands of years later gold is still being used for fillings, crowns, bridges and orthodontic appliances. Gold is a bio-compatible metal, meaning it can be placed in contact with a person’s body and not cause harm to one’s health.
Thousands of years later gold is still being used for fillings, crowns, bridges and orthodontic appliances. Gold is a bio-compatible metal, meaning it can be placed in contact with a person’s body and not cause harm to one’s health.
 Gold is a highly efficient conductor of electricity and is used in most electronic devices, including cell phones. Gold contained in connectors, switches and relay contacts allows phones to remain free of corrosion.
Gold is a highly efficient conductor of electricity and is used in most electronic devices, including cell phones. Gold contained in connectors, switches and relay contacts allows phones to remain free of corrosion.
 According to the World Gold Council, a single mobile device contains up to 50 milligrams of gold. That’s a tiny amount but nearly 1 billion cell phones are produced each year. With a gold value of about 50 cents in each phone, that adds up to $500 million dollars in gold each year!
According to the World Gold Council, a single mobile device contains up to 50 milligrams of gold. That’s a tiny amount but nearly 1 billion cell phones are produced each year. With a gold value of about 50 cents in each phone, that adds up to $500 million dollars in gold each year!
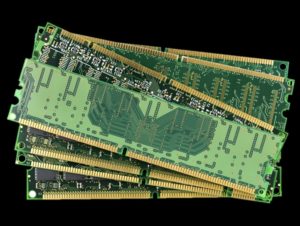 Gold can also be found in most standard desktop and laptop computers. The precious metal is used in a CPU’s memory chip and motherboard, allowing parts of your computer to receive power and communicate with each other.
Gold can also be found in most standard desktop and laptop computers. The precious metal is used in a CPU’s memory chip and motherboard, allowing parts of your computer to receive power and communicate with each other.
 Gold acts as a reliable conductor, allowing for the rapid and accurate transmission of digital data from one device to another. In fact, only silver and copper are better conductors of electricity.
Gold acts as a reliable conductor, allowing for the rapid and accurate transmission of digital data from one device to another. In fact, only silver and copper are better conductors of electricity.
 The earliest medical use of gold can be traced back to China in 2500 BC. Chinese physicians used pure gold to treat furuncles, smallpox, skin ulcers and to remove mercury from skin and flesh, says GoldBulletin.
The earliest medical use of gold can be traced back to China in 2500 BC. Chinese physicians used pure gold to treat furuncles, smallpox, skin ulcers and to remove mercury from skin and flesh, says GoldBulletin.
 Today the metal is primarily used to treat patients with arthritis. Gold salts are used to reduce swelling, bone damage and to relieve joint pain and stiffness. It’s a slow process; patients generally receive 22 weeks of gold injections before experiencing relief.
Today the metal is primarily used to treat patients with arthritis. Gold salts are used to reduce swelling, bone damage and to relieve joint pain and stiffness. It’s a slow process; patients generally receive 22 weeks of gold injections before experiencing relief. 
Gold is highly malleable and flexible. Gold can be beaten into thin sheets, only a few millionths of an inch thick. These sheets, known as gold leaf, are displayed on buildings throughout the world, such as St. Michael’s Cathedral in Kiev, Ukraine.
 India’s Sripuram Golden Temple is the world’s largest golden structure. The spiritual park is made out of 1.5 tons of gold. The gold leafing provides a durable and corrosion-resistant covering, says GoldPrice.com.
India’s Sripuram Golden Temple is the world’s largest golden structure. The spiritual park is made out of 1.5 tons of gold. The gold leafing provides a durable and corrosion-resistant covering, says GoldPrice.com.
 It’s truly a gold universe. Space vehicles are fitted with gold-coated polyester film to reflect infrared radiation and to help stabilize core temperatures, says Geology.com. Without gold, darker colored parts of spacecraft would absorb significant amounts of heat.
It’s truly a gold universe. Space vehicles are fitted with gold-coated polyester film to reflect infrared radiation and to help stabilize core temperatures, says Geology.com. Without gold, darker colored parts of spacecraft would absorb significant amounts of heat.
 NASA also protects its astronauts using gold. Astronauts’ helmets are covered by the extravehicular visor assembly. The visor is coated with a thin layer of gold to filter out the sun’s harmful rays, according to NASA.
NASA also protects its astronauts using gold. Astronauts’ helmets are covered by the extravehicular visor assembly. The visor is coated with a thin layer of gold to filter out the sun’s harmful rays, according to NASA.
Source: http://www.usfunds.com/slideshows/the-many-uses-of-gold/#.WCEhQvTa5Tx

